In this assignment, the goal is to evaluate the quality of educational multimedia resources by using a theory assessment rubric. The rubric is well designed to evaluate different qualities to examine how design choices impact learning. By using the key element of multimedia learning theory, active learning, and accessibility and Universal Design for Learning, this will help evaluate different qualities of educational resources
Multimedia Educational Resource Assessment Rubric
| Criteria | 0-2 Need Additional work | 3 Marginally Meet Expectation | 4 Fully Meet Expectation | 5 Exceeds Expectation |
| Theories of Multimedia Critique | Multimedia elements have little connection to CTML principles. Key principles are violated, increasing cognitive load. Design issues cause overload or confusion | Multimedia elements are present, but some principles are missing or may be inconsistently applied | Multimedia design accurately and intentionally employs various CTML principles to support learning. Visual and auditory elements complement each other, reducing factors that hinder learning | Multimedia elements have a strong connection to CTML principles. Key principles are not violated. Well-designed materials that help maximize understanding through the purposeful integration of media |
| Active Learning and Cognitive Engagement | Learners are in a passive state, with little practice and feedback. There is a lack of opportunities for interaction, communication, or application | Learners are in a passive position or have limited opportunities to participate. The learning path includes some opportunities for interaction, communication, or application, but these are very few. | Clear positive learning elements. The learning path is well-structured with scaffolding and extension challenges, and provides opportunities for interaction, communication, and application, but there is still room for improvement. | Learners are actively engaged in the learning process. The learning path offers well-developed, tiered instruction and extended challenges, and includes opportunities for interaction, communication, and application. |
| Accessibility and Universal Design for Learning | Accessibility features are missing or minimal, subtitles are lacking or navigation is poor, resulting in a poor learning experience. | The system has very few auxiliary functions, the subtitles do not match the content, and the learner’s needs are not being met. | Meet key accessibility requirements and provide accessible navigation to support most types of learners. Clear structure and conforms to UDL principles. | Strong inclusive design and provide accessible navigation to support all types of learners. Clear structure and conforms to UDL principles. |
| Clarity of Instruction and Instructional Intent | The purpose and learning goal are unclear. The contents are confusing and disconnected | The purpose and learning goal are implied but need more scaffolding. The contents cause some confusion and disconnected | The learning objectives are clear but not specific enough. Appropriate guidance is needed to help learners understand them. | The learning objectives are clear and specific. Strong guidance helps learners understand the objectives and promotes concept development. |
Located Educational Resources
- Format: Recorded lecture
- Visuals: Mostly instructional visuals
- Interaction: Low since viewers mainly watch or listen
- Presentation Style: Moves through definitions with slides that include a few images but a lot of text and number
- Audience Engagement: Lengthy lecture format and limited interaction

| Criteria | 0-2 Need Additional work | 3 Marginally Meet Expectation | 4 Fully Meet Expectation | 5 Exceeds Expectation |
| Theories of Multimedia Critique | This resource relies almost entirely on text and numbers. There are only a few images, but heavy text, particularly for abstract mathematical ideas. | Multimedia elements are present, but some principles are missing or may be inconsistently applied | Multimedia design accurately and intentionally employs various CTML principles to support learning. Visual and auditory elements complement each other, reducing factors that hinder learning | Multimedia elements have a strong connection to CTML principles. Key principles are not violated. Well-designed materials that help maximize understanding through the purposeful integration of media |
| Active Learning and Cognitive Engagement | Learners are in a passive state, since the speaker only moves point to point. Question by question There is no active learning and cognitive engagement | Learners are in a passive position or have limited opportunities to participate. The learning path includes some opportunities for interaction, communication, or application, but these are very few. | Clear positive learning elements. The learning path is well-structured with scaffolding and extension challenges, and provides opportunities for interaction, communication, and application, but there is still room for improvement. | Learners are actively engaged in the learning process. The learning path offers well-developed, tiered instruction and extended challenges, and includes opportunities for interaction, communication, and application. |
| Accessibility and Universal Design for Learning | There are only texts and numbers in the whole learning process. | The system has very few auxiliary functions, the subtitles do not match the content, and the learner’s needs are not being met. | Meet key accessibility requirements and provide accessible navigation to support most types of learners. Clear structure and conforms to UDL principles. | Strong inclusive design and provide accessible navigation to support all types of learners. Clear structure and conforms to UDL principles. |
| Clarity of Instruction and Instructional Intent | The purpose and learning goal are unclear. The contents are confusing and disconnected | The purpose and learning goal are help student have a better understand in Economic concept but is hard for student to follow since the information are too heavy | The learning objectives are clear but not specific enough. Appropriate guidance is needed to help learners understand them. | The learning objectives are clear and specific. Strong guidance helps learners understand the objectives and promotes concept development. |
Overall Evaluation/justification:
Overall, this method of teaching is a bad example in Multimedia Educational Resource. The lecture video explains what poverty is and the problems that poverty causes. The speaker moves from point to point and explains the content using slides and text. This is a passive learning style in which students are only able to listen or watch. When they have questions, there is no platform for them to ask, which is not beneficial for students. Moreover, the video is too long and has too many texts and numbers. Moreover, due to a lack of images and a lack of animation, it will reduce accessibility. Therefore, this method of learning is mostly passive viewing rather than active learning.
- Format: Design in different short videos (around 15mins), each video focuses on one concept only. Help the learner to focus on one thing at a time.
- Visuals: on-screen text, diagrams and animations.
- Interaction: There will be a Q&A section, and people can ask questions.
- Presentation Style: Design in different short videos with captions
- Audience Engagement: The videos are short, therefore learner to focus on the lesson itself. There are some quizes for learners to participate in different sections

| Criteria | 0-2 Need Additional work | 3 Marginally Meet Expectation | 4 Fully Meet Expectation | 5 Exceeds Expectation |
| Theories of Multimedia Critique | Multimedia elements have little connection to CTML principles. Key principles are violated, increasing cognitive load. Design issues cause overload or confusion | Multimedia elements are present, but some principles are missing or may be inconsistently applied | Text, images, and videos are combined in this resource, and the content is organized into different topics. This structure helps learners quickly understand the purpose of the resources and their starting point, thereby reducing confusion and unnecessary cognitive burden. | Multimedia elements have a strong connection to CTML principles. Key principles are not violated. Well-designed materials that help maximize understanding through the purposeful integration of media |
| Active Learning and Cognitive Engagement | Learners are in a passive state, with little practice and feedback. There is a lack of opportunities for interaction, communication, or application | Learners go through a clear sequence of watching, trying, and receiving feedback, and the complexity of the task increases over time. | Clear positive learning elements. The learning path is well-structured with scaffolding and extension challenges, and provides opportunities for interaction, communication, and application, but there is still room for improvement. | Learners are actively engaged in the learning process. The learning path offers well-developed, tiered instruction and extended challenges, and includes opportunities for interaction, communication, and application. |
| Accessibility and Universal Design for Learning | Accessibility features are missing or minimal, subtitles are lacking or navigation is poor, resulting in a poor learning experience. | The system has very few auxiliary functions, the subtitles do not match the content, and the learner’s needs are not being met. | There are images with texts, and the video also includes the transcript below, which provides help for different students with different needs. | Strong inclusive design and provide accessible navigation to support all types of learners. Clear structure and conforms to UDL principles. |
| Clarity of Instruction and Instructional Intent | The purpose and learning goal are unclear. The contents are confusing and disconnected | The purpose and learning goal are implied but need more scaffolding. The contents cause some confusion and disconnected | The learning objectives are clear but not specific enough. Appropriate guidance is needed to help learners understand them. | The learning objectives are clear, and the learning is progressive. Students can learn one different concept at a time. |
Overall Evaluation/justification:
This educational resource has a clear structure, which is easy for teachers to use. It provides thorough explanations. The multimedia supports most types of learners since it includes short videos with transcripts. Overall, I would say this is a great resource for students. Using short videos (around 10–15 minutes) that focus on one topic helps students stay focused. Moreover, the videos include some animation and captions, which can help students understand better. However, the interactive learning section is mostly limited to multiple-choice questions and lacks in-depth interactive or constructive tasks. Therefore in the Active Learning and Cognitive Engagement section, there will be some improvement for this resource.
Format: Design in different short videos (around 10-15 mins), each video focuses on one concept, after each video, there will be a game to text leaner knowledge
Visuals: on-screen text, simple diagrams and funny animations.
Interaction: There will be Q&A and games sections, and learners can ask questions after each section.
Presentation Style: Design in different short videos with captions and animations
Audience Engagement: The videos are short, therefore learner to focus on the lesson itself. There are some games for learners to participate in different sections


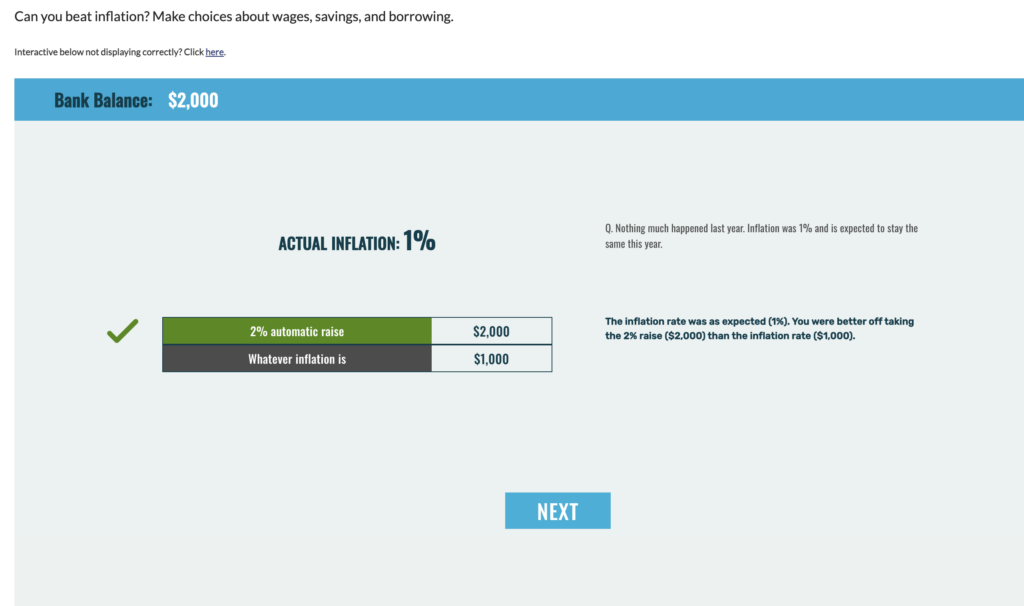
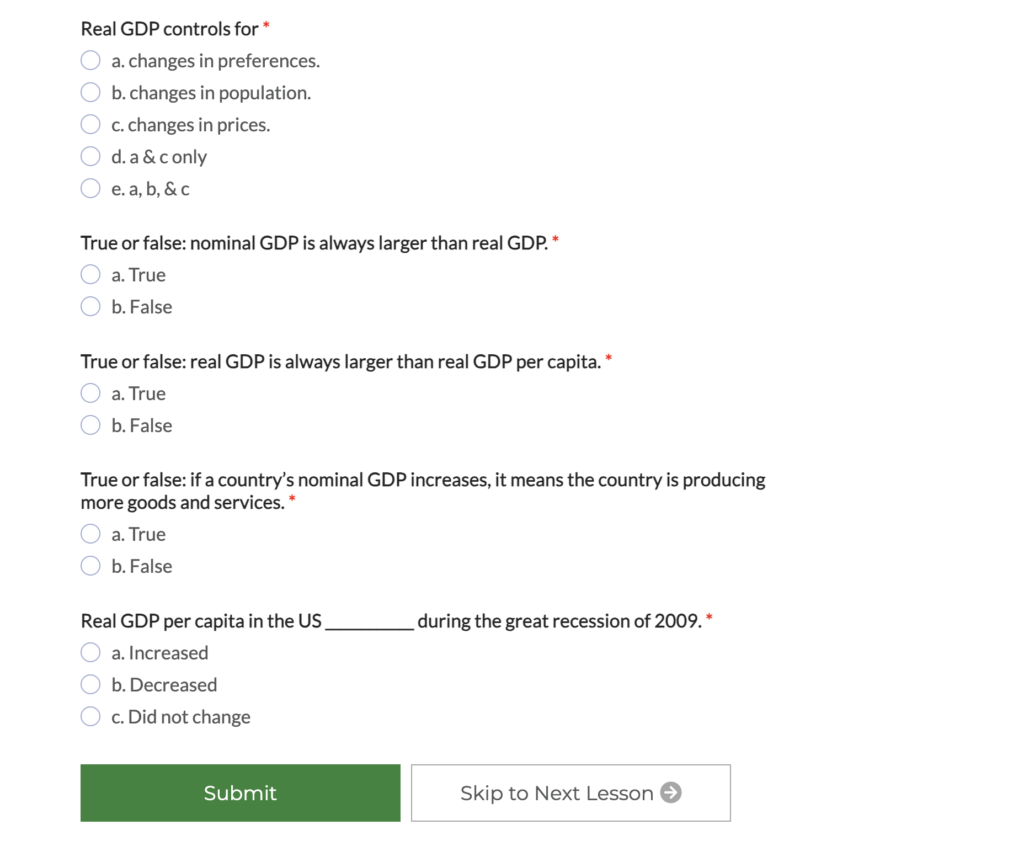
| Criteria | 0-2 Need Additional work | 3 Marginally Meet Expectation | 4 Fully Meet Expectation | 5 Exceeds Expectation |
| Theories of Multimedia Critique | Multimedia elements have little connection to CTML principles. Key principles are violated, increasing cognitive load. Design issues cause overload or confusion | Multimedia elements are present, but some principles are missing or may be inconsistently applied | Multimedia design accurately and intentionally employs various CTML principles to support learning. Visual and auditory elements complement each other, reducing factors that hinder learning | Text, images, videos and animation are combined in this educational resource, and the content is organized into different topics. This structure helps learners quickly understand the purpose of the resources and their starting point, thereby reducing confusion and unnecessary cognitive burden. |
| Active Learning and Cognitive Engagement | Learners are in a passive state, with little practice and feedback. There is a lack of opportunities for interaction, communication, or application | Learners are in a passive position or have limited opportunities to participate. The learning path includes some opportunities for interaction, communication, or application, but these are very few. | Clear positive learning elements. The learning path is well-structured with scaffolding and extension challenges, and provides opportunities for interaction, communication, and application, but there is still room for improvement. | There are different sections, which include the game model, quiz, video induction, and images. Those can help students to be more active in learning and improve the cognitive engagement. |
| Accessibility and Universal Design for Learning | Accessibility features are missing or minimal, subtitles are lacking or navigation is poor, resulting in a poor learning experience. | The system has very few auxiliary functions, the subtitles do not match the content, and the learner’s needs are not being met. | Meet key accessibility requirements and provide accessible navigation to support most types of learners. Clear structure and conforms to UDL principles. | There are images and animations with texts, and the video also includes the transcript below, which provides help for different students with different needs. |
| Clarity of Instruction and Instructional Intent | The purpose and learning goal are unclear. The contents are confusing and disconnected | The purpose and learning goal are implied but need more scaffolding. The contents cause some confusion and disconnected | The learning objectives are clear but not specific enough. Appropriate guidance is needed to help learners understand them. | The learning objectives are strong and clear, and the learning is progressive. Students can learn one different concept at a time. |
Overall Evaluation/justification:
This is a great example of educational resources. I have given 20 out of 20 for this resource. First, it has a clear goal and well-designed structures. It will be beneficial for all kinds of learners since it has well designed and accessible. Since there is a clear and simple image, text, animation and number, which can met leaner with different needs. The goal of the educational resource is clear and easy to understand, which can help learners have a better understand in Economic concepts. From the evidence, we can see that the learning process is very diversified, including image, video, text, game, and quiz. Therefore, it will help students in active learning and have a better cognitive engagement. It supports teachers and learners, and it includes great in-depth interactive or constructive tasks. Students are able to ask questions after each section, and there will be a section for testing learner learning outcomes, and it will show the result to the teacher. Therefore, this will maximize the learning effectiveness and experience.
Resources:
BurkeyAcademy. (n.d.). Poverty: Measurements, meaning, and alleviation (Updated) [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BeH1N1UfvFc
Federal Reserve Education. (n.d.). Economic Lowdown video series. Retrieved February 5, 2026, from https://www.federalreserveeducation.org/teaching-resources/economics/series/economic-lowdown-video-series
Marginal Revolution University. (n.d.). Basic facts of wealth. Retrieved February 5, 2026, from https://mru.org/courses/principles-economics-macroeconomics/gdp-per-capita-purchasing-power-parity-example
Leave a Reply